Chemistry Journal of Moldova
ANTIOXIDANT PROPERTIES OF SOME PLANT EXTRACTS AND EFFECT OF THEIR ADDITION ON THE OXIDATION STABILITY OF BIODIESEL
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 35-44
Pavlo Kuzema, Iryna Laguta, Oksana Stavinskaya, Viktor Anishchenko, Anastasiia Kramar, Natalia Smirnova, Tetiana Fesenko, Roman Ivannikov, Oksana Linnik
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 35-44
plant extract, phenolic compound, antioxidant, biodiesel, oxidation stability.
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The extracts from the leaves of Deschampsia antarctica, Camelina sativa, and Camellia japonica plants, as well as from Camelina sativa and Silybum marianum seedcakes were investigated as potential additives for improvement of biodiesel stability against oxidation. In spite of significant distinctions in the content of various phenolic compounds, all the extracts were found to effectively inhibit DPPH radicals and decelerate transformation of fatty acid esters of biodiesel into organic acids by ~9-26%. Various extracts were shown to have different activity towards the biodiesel from rape and camelina seed oils; this result is consistent with the assumption that there is no universal stabilizer for different types of biodiesel.
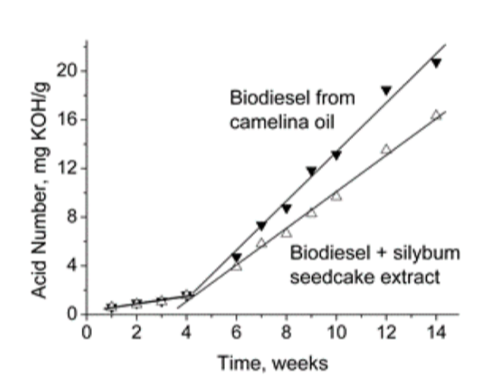
Graphical Abstract: The extracts from the leaves of Deschampsia antarctica, Camelina sativa, and Camellia japonica plants, as well as from Camelina sativa and Silybum marianum seedcakes were investigated as potential additives for improvement of biodiesel stability against oxidation. In spite of significant distinctions in the content of various phenolic compounds, all the extracts were found to effectively inhibit DPPH radicals and decelerate transformation of fatty acid esters of biodiesel into organic acids by ~9-26%. Various extracts were shown to have different activity towards the biodiesel from rape and camelina seed oils; this result is consistent with the assumption that there is no universal stabilizer for different types of biodiesel.

Downloads: 128






