Chemistry Journal of Moldova
SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND MOLECULAR DOCKING OF CHLORO-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYXANTHONE DERIVATIVES
Author(s):
Field: Organic chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2019 Volume 14, no.1
Pages: 68-76
Emmy Yuanita, Harno Dwi Pranowo, Mustofa Mustofa, Respati Tri Swasono, Jufrizal Syahri, Jumina Jumina
Field: Organic chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2019 Volume 14, no.1
Pages: 68-76
chlorination, chloro-substituted hydroxyxanthone, derivative, anticancer, molecular docking.
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: In this study, the chloro-substituted hydroxyxanthones were prepared by cyclodehydration of acid derivatives and substituted phenol in the presence of Eaton reagent, followed by halogenations step to electrophilic substitution of chlorine in a moderate yield. The in vitro anticancer activity study on various cell lines revealed that the chloro functional group increases the anticancer activity of the hydroxyxanthone derivatives. The molecular docking study showed that there was a binding interaction between chloro-hydroxyxanthone and the amino acid residues such as Asp810, Cys809, Ile789, His790, and Leu644 of protein tyrosine kinase receptor.
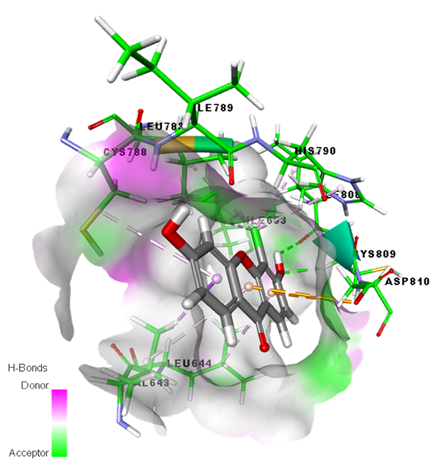
Graphical Abstract: In this study, the chloro-substituted hydroxyxanthones were prepared by cyclodehydration of acid derivatives and substituted phenol in the presence of Eaton reagent, followed by halogenations step to electrophilic substitution of chlorine in a moderate yield. The in vitro anticancer activity study on various cell lines revealed that the chloro functional group increases the anticancer activity of the hydroxyxanthone derivatives. The molecular docking study showed that there was a binding interaction between chloro-hydroxyxanthone and the amino acid residues such as Asp810, Cys809, Ile789, His790, and Leu644 of protein tyrosine kinase receptor.

Downloads: 616






