Chemistry Journal of Moldova
2025 Volume 20, no.1
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 17-27
Maxim Cisteacov, Gheorghe Duca, Vladislav Blonschi, Viorica Gladchi, Angela Lis, Elena Bunduchi
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 17-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
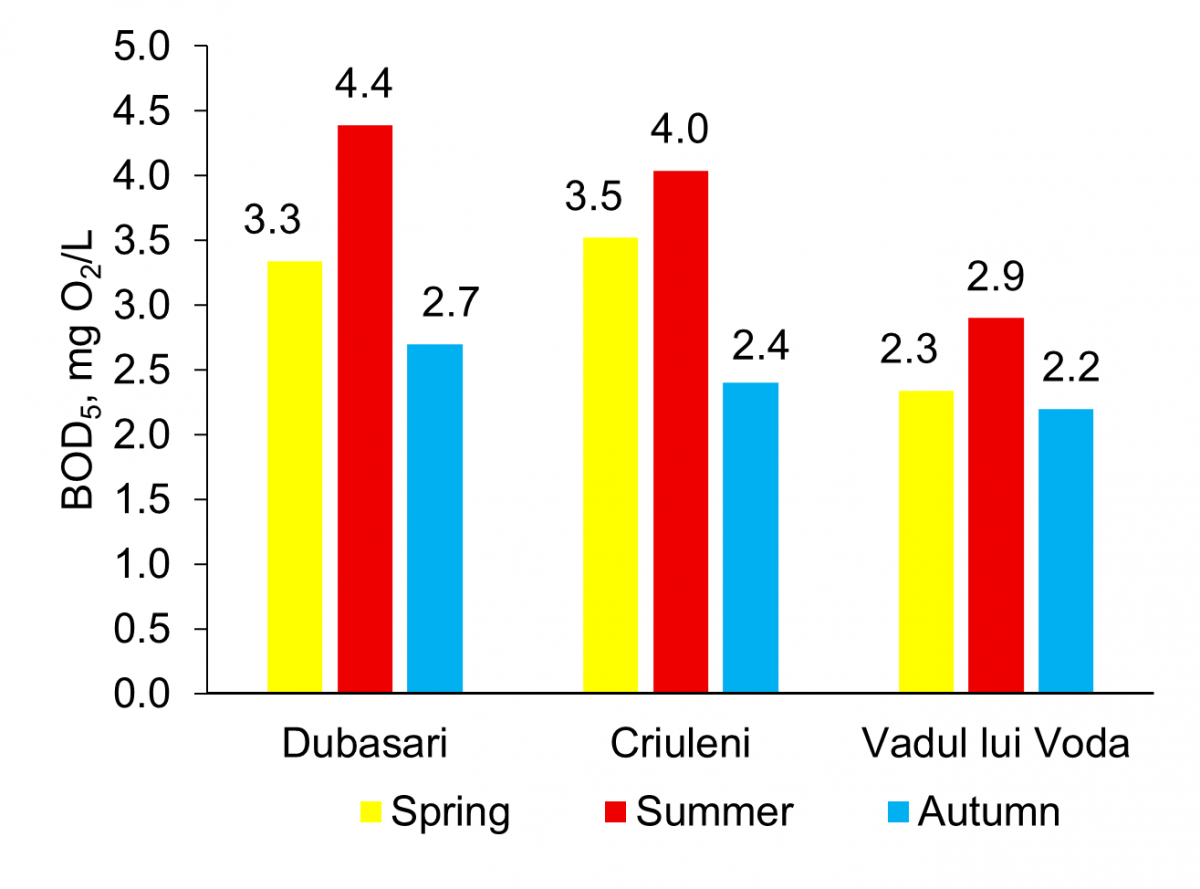
Graphycal Abstract: The study represents an analysis of the dynamics of self-purification processes in the Dniester River waters over ten years, conducted based on five hydrochemical and kinetic parameters. The study results demonstrated that the Dniester River waters are also loaded with reducing compounds, especially from the Răut and Ichel tributaries, which diminishes the intensity of the self-purification processes. However, after the last sampling point, a slight trend toward restoring initial properties was observed.
Downloads: 167
Author(s):
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 51-61
Abhimanyu Parasram Pawar, Kishor Sudhir Naktode, Arvind Janardhan Mungole, Srinivas Angac
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 51-61
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1308
Graphycal Abstract: Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were synthesized using Nicotiana plumbaginifolia plant extract through a green approach. XRD, FTIR, and EDX confirmed their hexagonal wurtzite structure and high purity. SEM and TEM showed spherical ZnO NPs (16–24 nm), with a band gap of 3.33 eV. FTIR spectra displayed a peak at 480 cm⁻¹, confirming Zn–O bond formation. The ZnO NPs exhibited strong antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa, E. coli,
K. pneumoniae, and S. aureus at 100 µL using the well diffusion method. They also showed excellent antioxidant potential, scavenging DPPH radicals with 75.59% inhibition at 250 μg/mL. This eco-friendly synthesis method offers a sustainable approach for ZnO NP production, highlighting their potential for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications.
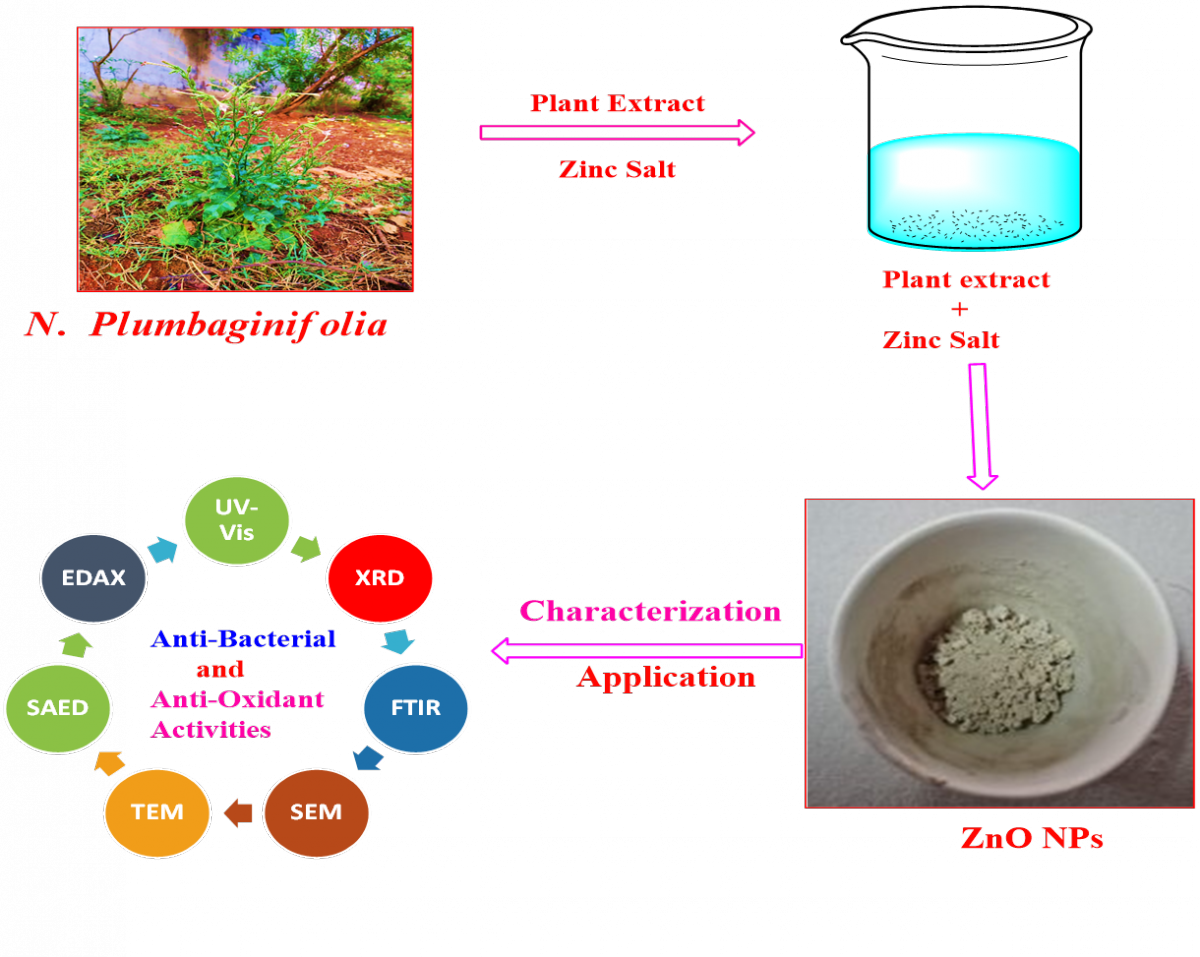
K. pneumoniae, and S. aureus at 100 µL using the well diffusion method. They also showed excellent antioxidant potential, scavenging DPPH radicals with 75.59% inhibition at 250 μg/mL. This eco-friendly synthesis method offers a sustainable approach for ZnO NP production, highlighting their potential for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications.

Downloads: 118
Author(s):
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 100-105
Daniel Cord, Mirela Claudia Rimbu, Cristiana Tanase, Cristina Tablet, Gheorghe Duca
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 100-105
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1337
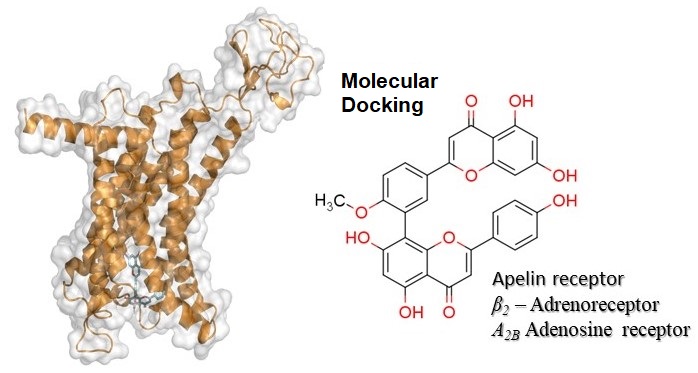
Graphycal Abstract: Interactions between various natural compounds and three selected G protein coupled receptors were investigated through molecular docking. The strongest binding affinities were identified highlighting potential modulators for these receptors.
Downloads: 104
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 69-78
Ihor Pylypenko, Iryna Kovalchuk, Mykola Tsyba, Yurii Lytvynenko, Oleksandr Shyrokov
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 69-78
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1294
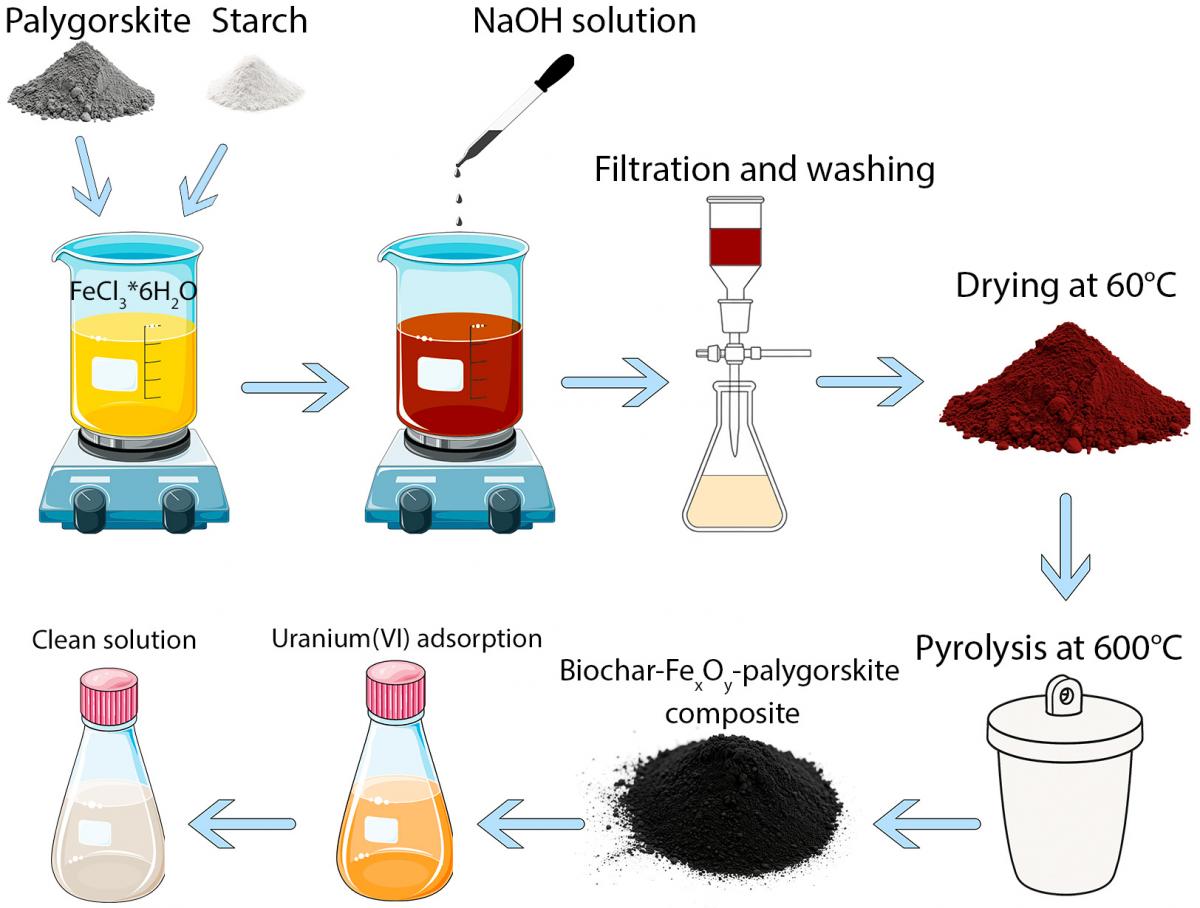
Graphycal Abstract: This paper presents palygorskite/biochar/iron oxide composites for uranium (VI) removal from water. The composites, containing magnetite and hematite, achieved maximum uranium adsorption (100.2 μmol/g), with pH increase enhancing the process. Magnetite facilitated uranium (VI) reduction to uranium (IV), proving effective for in situ water remediation.

Downloads: 79
Author(s):
Field: Organic chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 62-68
Stefan Robu, Tamara Potlog, Ion Bulimestru, Ion Lungu, Olga Sadohina, Alexandrina Druta, Petru Bulmaga, Iacob Gutu
Field: Organic chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 62-68
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1217
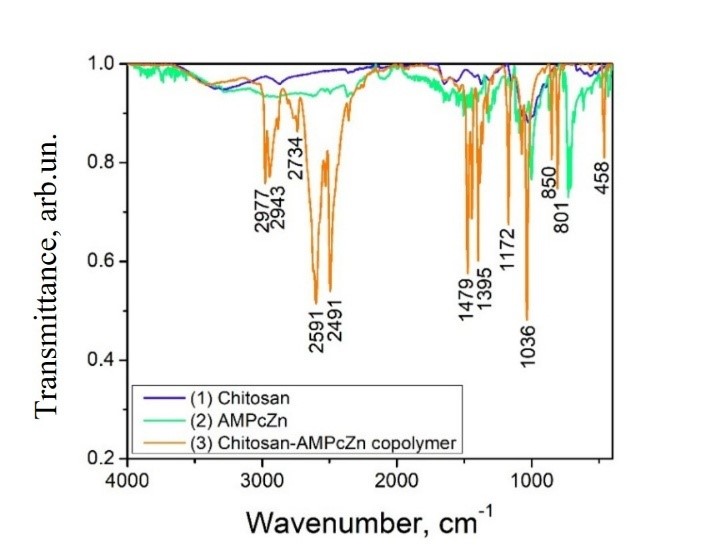
Graphycal Abstract: This study presents the synthesis of a novel polymer analogue derived from aminomethyl zinc phthalocyanine (AmPcZn) and chitosan (CH). The polymer was produced by grafting AmPcZn onto chitosan using ethyl chloroformate as a coupling agent. The resulting CH–AmPcZn polymers, containing 10%, 20%, 30%, and 60% AmPcZn, were characterized using FTIR and UV-Vis spectroscopy. The UV-Vis analysis showed that absorbance increased with higher concentrations of AmPcZn in the CH–AmPcZn solutions.

Downloads: 72
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 7-16
Abdelghani Mahmoudi and Silvia De Francia
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 7-16
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1312
Graphycal Abstract: Novel spectrophotometric method and bioassay using the Bacillus subtilis strain were developed for clarithromycin analysis. Experimental conditions were optimised and validated according to ICH guidelines. A comparative study was established, and the methods were successfully applied for the quantification of clarithromycin in solid dosage forms and can be used for pharmaceutical purposes.

Downloads: 67
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Inna Trus, Vita Halysh, Mariia Tverdokhlib, Olena Makarenko, Evhen Chuprinov, Vadim Fedin
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Full Text (PDF): Download
Graphycal Abstract: A promising method of water conditioning for water circulation systems with the use of a scale stabiliser was considered. To inhibit the scale formation, antiscalant RT-2024-4 was used and the ability to mitigate the scale formation was tested. Water of various origins with different hardness was used during experiments.

Downloads: 56
Author(s):
Field: Industrial chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 38-50
Thanh Thuy Tran Thi, Thanh Nha Tran Thi, AnhThi Hoang, VanTrong Nguyen
Field: Industrial chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 38-50
Full Text (PDF): Download
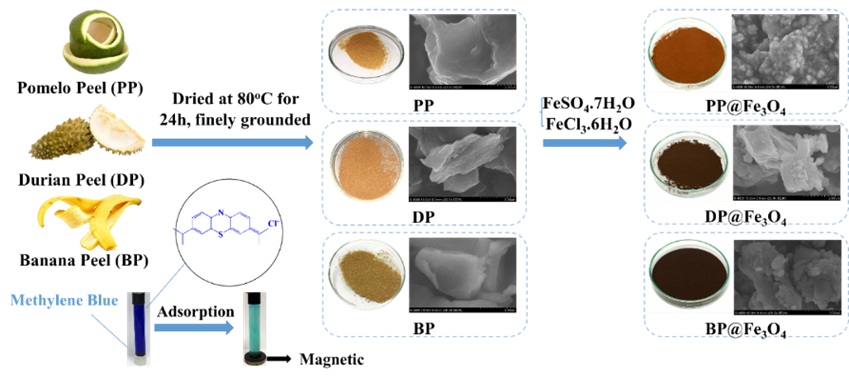
Graphycal Abstract: The magnetic materials were synthesised from pomelo peel (PP@Fe3O4), durian peel (DP@Fe3O4), and banana peel (BP@Fe3O4) for adsorption of Methylene Blue. Under the optimal conditions, adsorption efficiencies of 97.7%, 97%, and 98.9%, respectively. These materials were employed to assess the COD index in select water samples.

Downloads: 98
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 79-85
Latifah Hauli, Chika Lutfi Adiningrum, Muhammad Safaat, Indri Badria Adilina, Silvester Tursiloadi, Lenny Marlinda, Dian Susanthy, Muflikhah Muflikhah
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 79-85
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1279
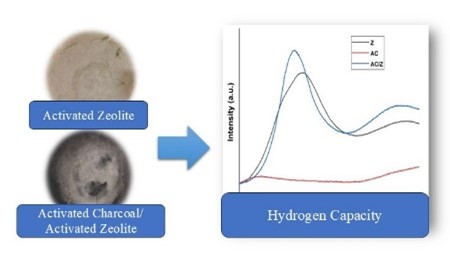
Graphycal Abstract: The purpose of this research was to activate Lampung natural zeolites, modify them with activated charcoal, and evaluate how well they store hydrogen. The highest hydrogen capacity value, 0.57 mmol/g, is found in activated natural zeolite, according to the Hydrogen-temperature programmed desorption data (H2-TPD).

Downloads: 45
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 95-99
Olha Khudoiarova, Oleg Blazhko, Alina Blazhko
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 95-99
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1250
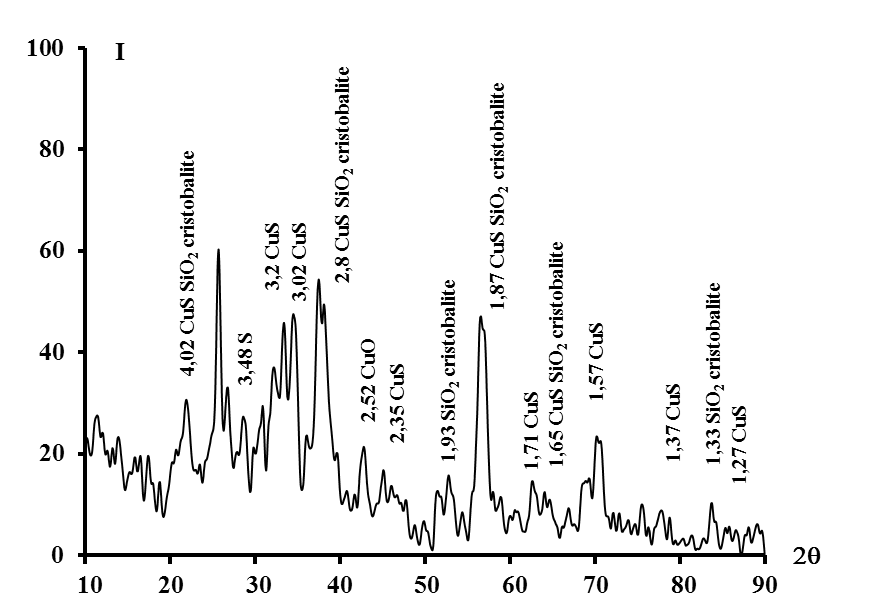
Graphycal Abstract: The effectiveness and prospects of using food industry waste sorbents for water purification from copper (II) ions have been studied. The use of a regenerated sorbent made of activated carbon and kieselguhr modified with sulphide and hydrosulphide ions increases the efficiency of removing copper (II) cations from water by 65.5 times It was established that topochemical reactions occur on the surface of the modified sorbent with the formation of copper (II) sulphide CuS and elemental sulfur. The possibility of topochemical transformations was established by IR-spectral and X-ray phase studies.

Downloads: 55






