Chemistry Journal of Moldova
PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND BIOACTIVITIES OF DIFFERENT ORGANS OF BUNIUM FERULACEUM SM.
Author(s):
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 65-71
Achraf Khaldi, Abdelkader Elhadj Berrezig, Amina Mazeri, Kheira Mehdi, Rahima Hadjer Gouabi
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 65-71
Bunium ferulaceum Sm., phytochemical analysis, anti-inflammatory activity, antibacterial activity.
Full Text (PDF): Download
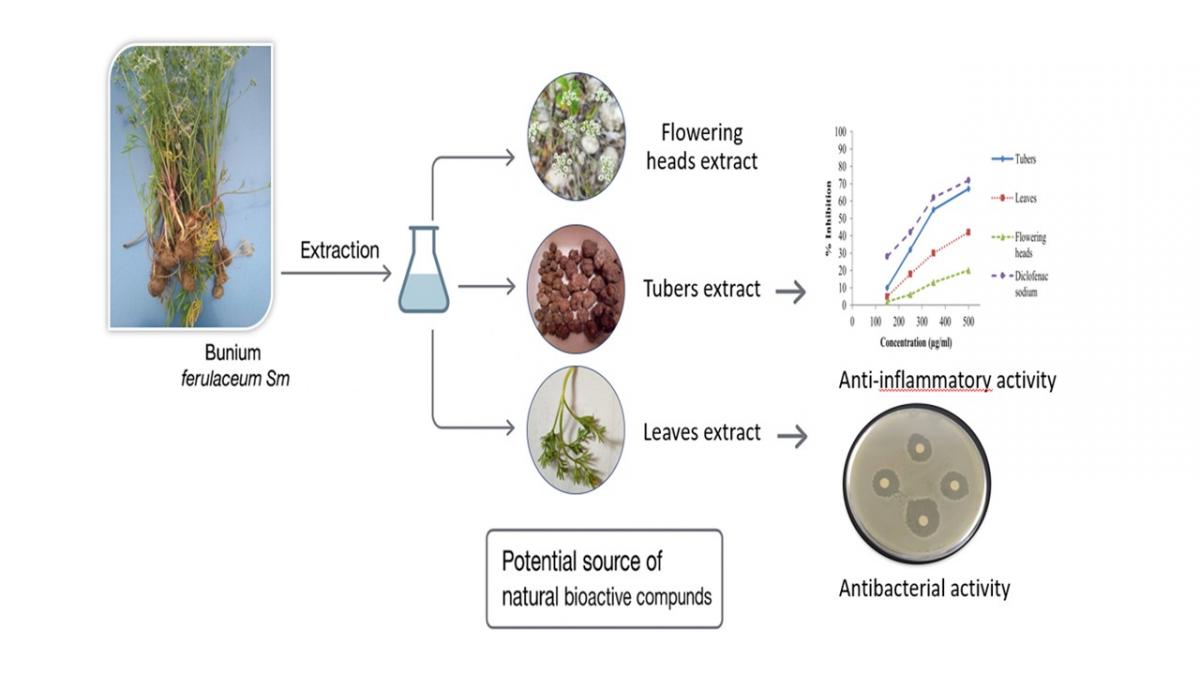
Graphycal Abstract: Hydro-methanolic extracts of Bunium ferulaceum leaves, flowering heads, and tubers show organ-dependent phytochemical variation. Leaves are richest in phenolics and flavonoids, while tubers contain the highest triterpene levels. Polyphenol content correlates strongly with antibacterial activity, whereas triterpenes are tightly linked to anti-inflammatory effects. These complementary chemical–biological relationships highlight the plant’s multifunctional pharmacological potential, supporting further isolation and mechanistic studies.

Downloads: 48






