Chemistry Journal of Moldova
SYNTHESYS AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HETEROMETALLIC {[FeCa2(Sal)2(SalH)3(DMA)2(CH3OH)2]}n SALICYLATE COMPLEX
Author(s):
Field: Inorganic and coordination chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 62-68
Viorina Gorinchoy, Olesea Cuzan, Sergiu Shova, Vasile Lozan
Field: Inorganic and coordination chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 62-68
oxo-carboxylate, iron(III), calcium(II), heteronuclear cluster, salicylic acid, s-d metals.
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1168
Abstract (PDF)
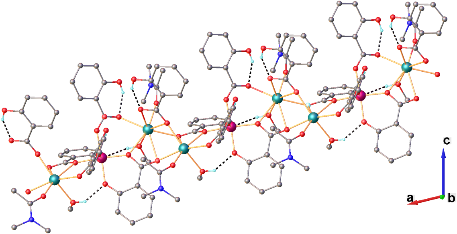
Graphical Abstract: A new heterometallic iron(III) compound, derivative of salicylic acid, catena–poly[bis(methanol)-bis(N,N–dimethylacetamide)–tris(m–salicylato)–bis(m–salicyl)–dicalcium(II) iron(III)], has been synthesized and characterized by infrared spectroscopy, single-crystal X-ray diffraction and elemental analysis. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction study revealed that synthesized compound forms an 1D coordination polymer with general formula {[FeCa2(Sal)2(SalH)3 (DMA)2(CH3OH)2]}n. The compound crystallizes in the P21/c space group of the monoclinic system with the following unit cell parameters: а= 9.76785(9), b= 37.3386(4), c= 13.82575(12) Å, β= 103.6421(9)°, Z= 4. The independent unit cell of the obtained compound contains one iron and two calcium ions, in which the iron(III) ion has an octahedral coordination sphere. The different coordination modes of the five molecules of salicylic anions revealed by IR analysis were confirmed by X-ray studies, showing that the salicylate anions play the role of bridging ligands and coordinate in three different ways, thus the carboxylic group forms bridges through three different coordination pathways, namely: bidentate, tridentate and pentadentate fashion.
Downloads: 110






