Chemistry Journal of Moldova
UNTANGLING THE INHIBITION EFFECTS OF ALIPHATIC AMINES ON SILVER CORROSION: A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2017 Volume 12, no.2
Pages: 64-70
Emre Topal, Gökhan Gece
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2017 Volume 12, no.2
Pages: 64-70
corrosion inhibitor, silver, aliphatic amines, density functional theory.
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2017.411
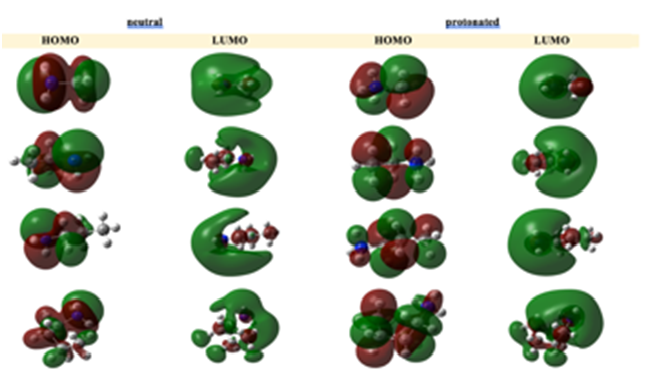
Graphical Abstract: The topic of corrosion inhibition of different metals by organic compounds has been the focus of intense scrutiny for decades. The enormity of the problem is reflected in the need to understand the underlying inhibition mechanisms of such compounds, one of which is the class of aliphatic amines. Electrochemical measurements represent protective effect of these compounds at ever-increasing levels of detail but these methods lack the resolution to represent inhibition efficiency-molecular structure relations adequately. In this study, the dependence of the inhibition effect of four aliphatic amines (methylamine, ethylamine, n-propylamine, and n-butylamine), on their molecular and electronic structure is analyzed using quantum chemical calculations. The obtained results of these calculations were found to be consistent with the experimental findings.

Downloads: 111






