Chemistry Journal of Moldova
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND BIOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF TRADITIONAL ALGERIAN PLANTS MELISSA OFFICINALIS L. AND URTICA DIOICA L.
Author(s):
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 45-55
Dahia Meridja, Kamel Belhamel, Mohamed Harrat, Chiraz Belhamel, Mohamed Yousfi
Field: Natural product chemistry and synthesis
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 45-55
Melissa officinalis L., Urtica dioica L., LC-MS/MS, antioxidant activity, anti-lithiatic activity.
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1328
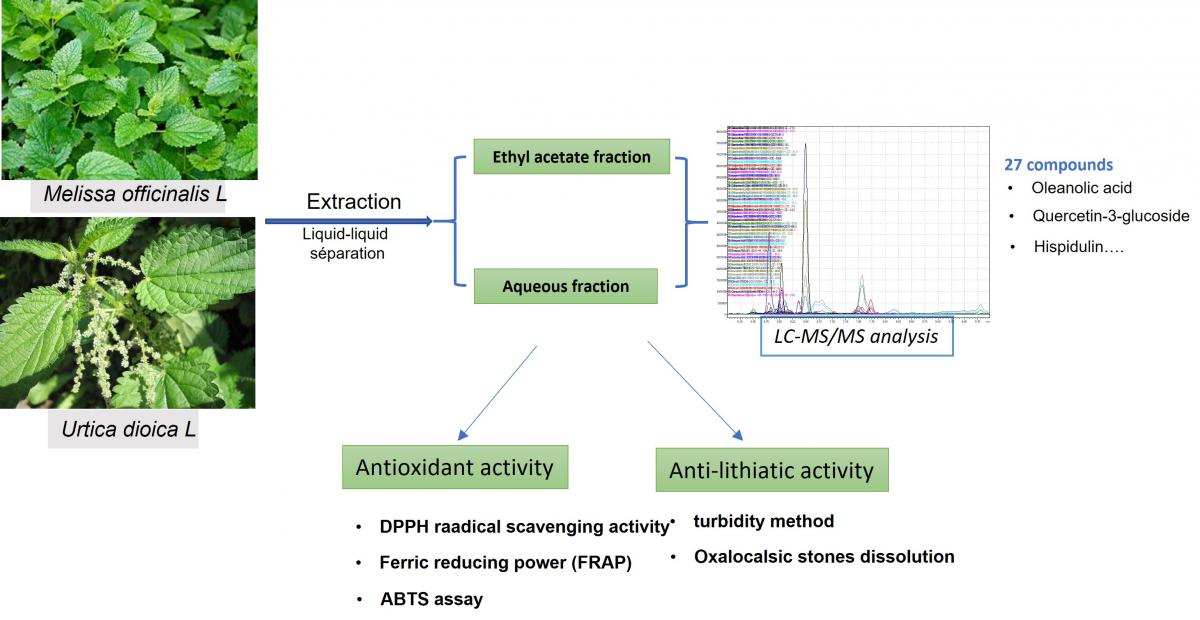
Graphycal Abstract: Melissa officinalis L. and Urtica dioica L. were evaluated for their phytochemical composition and antioxidant and anti-lithiatic activities. LC-MS/MS analysis showed that M. officinalis contained a more diverse profile, especially flavonoids and phenolic acids enriched in the ethyl acetate fraction, while U. dioica demonstrated a simpler composition dominated by myricetin, riboflavin, sinapic acid, catechin, and β-carotene in its aqueous fraction. M. officinalis ethyl acetate extract showed the strongest antioxidant capacity in DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. Its aqueous extract also exhibited notable anti-lithiatic activity, inhibiting calcium oxalate crystal formation by 87.12% at 2 mg/mL.

Downloads: 52






