Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Analytical chemistry
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2011 Volume 6, no.1
Pages: 45-51
Gheorghe Nemtoi, Liliana Airinei, Tudor Lupascu and Alexandru Cecal
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2011 Volume 6, no.1
Pages: 45-51
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2011.06(1).13
Graphical Abstract: The corrosion process of some steels immersed in HNO3 solutions of different concentrations by means of voltammetric measurements was investigated. For different values of the corrosion potential, or of the contact time: solid steel-aggressive medium, several equations of the type: I = f (E) were proposed, only for linear domains of the voltammograms.
Downloads: 20
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2009 Volume 4, no.2
Pages: 24-27
Ludmila Kiriyak, Natalia Cecoi, Tatiana Cazac, Mihail Revenco
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2009 Volume 4, no.2
Pages: 24-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2009.04(2).16
Graphical Abstract: The polarographic behavior of the complex formed by V(V) and 2,3–dihydroxybenzaldehyde (2,3–DHBA) in the solution containing acetate buffer (pH 5,2) has been investigated. By means of a.c. polarography, chronovoltammetry and other techniques, it has been shown that the electrode process is complicated by the adsorption of 2,3-DHBA and its vanadium complex. The kinetic and adsorption parameters of the electrode process have been determined: adsorption equilibrium constant B= 1,32⋅105 mol-1⋅dm3, the attraction constant γ = 1,2, the maximum surface concentration Гmax = 9,10⋅10-11 mol⋅ cm-2; the share of the electrode surface occupied by one particle of the adsorbed complex S = 1,81 nm2 and the free adsorption energy ΔG = - 39,1 kJ· mol-1.
Downloads: 16
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2009 Volume 4, no.1
Pages: 66-71
Cristina Dinu, Gabriela Vasile, Liliana Cruceru, Jana Petre
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2009 Volume 4, no.1
Pages: 66-71
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2009.04(1).11
Graphical Abstract: The European Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC), transposed in Romanian Legislation as Low 458/2002, amended by Low 311/2004, imposes the limit of concentration for metallic elements in water intended for human consumption. The toxic metals arsenic and selenium are among these elements and the limit value is 10 μg/L. In the paper there are presented the working conditions for determination of As and Se from drinking water using modern techniques based on the fl ow injection-hydride generation with the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (FIAS-ICP-EOS). The analyses were performed on Optima 5300 DV Perkin Elmer equipment with FIAS 400 Flow Injection System, Perkin Elmer type. For the hydride generation two types of solution were used: 10% (v/v) HCl as a carrier solution and 0.2 % NaBH4 in 0.05%NaOH solution as a reducing agent [1]. The treatment step of the samples and standard solutions consisted in reducing with mixed solutions of KI and ascorbic acid in acidic condition (HCl) for As and only with HCl and high temperature for Se [2,3]. The paper contains the characteristic parameters of the methods, such as: low detection limit, quantifi cation limit, repeatability, precision, recovery, which were evaluated using Certifi ed Reference Materials for each element.
Downloads: 20
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 52-55
Gheorghe Zgherea
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 52-55
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2008.03(1).02
Graphical Abstract: Mixtures of small quantities of carbonyl compounds are presents in foods, concerning sensorial qualities. The inferior carbonyl compounds (C2-C4, boiling point <100°C) – mono and dicarbonyl – can be identified and measured their concentrations, after a separation by distillation on the water bath. They are transferred in a strongly acid solution of 2.4-dinitrophenylhidrazine (2.4-DNPH), generating a mixture of insoluble 2.4-dinitrophenylhidrazones (2.4-DNPH-ones). The 2.4-DNPH-ones are organic compounds with weak polarity, solids, crystallized, yellows and water insoluble, soluble in organic solvents. The mixture of 2.4dinitrophenylhidrazones may be separated by liquid chromatography, using the reverse phase mechanism [1-3]. This paper contains experimental and theoretical considerations to the means of separation through liquid chromatography of two synthetically and a natural mixtures that contain 2.4-DNPH-ones provided by inferior carbonyl compounds; to obtain conclude results, in the synthetically mixtures was introduce and 2.4-DNPH-ones provided by carbonyl compounds having three (acetone and propanal) and four (isobutyl aldehyde) atoms of carbon.
Downloads: 23
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 48-51
Gheorghe Zgherea
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 48-51
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2008.03(1).03
Graphical Abstract: An equimolar mixture of 2.4-dinitrophenylhidrazones (2.4DNPH-ones) providing by acetaldehyde and diacetyl must be analyzed
Downloads: 12
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 44-47
Mihail Revenco, Mariana Martin, Waell A.A. Dayyih
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2008 Volume 3, no.1
Pages: 44-47
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (JPEG)
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2008.03(1).07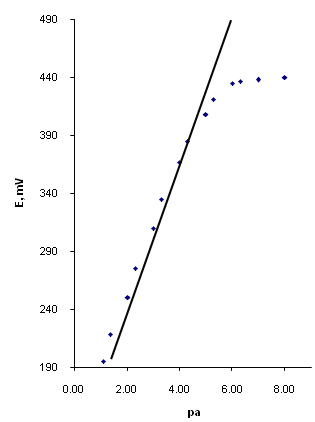
Graphical Abstract: The paper describes the analytical potentialities of the trinuclear chromium(III) complexes as potentiometric ionophores for the construction of electrodes sensitive to the presence of nitrate anion. The electroactive material containing 4,4’-bipyridil was synthesized in situ. The membrane was prepared using dioctylphthalate as a solvent mediator and poly (vinyl chloride) as a polymeric matrix. The electrodes presented a slope of 56 mV/decade, a low limit of detection (3,2.10-6 mol/l), an adequate lifetime (4 months), and suitable selectivity characteristics when compared with other nitrate electrodes. The good parameters of this electrode made possible its application to the determination of nitrate in different types of fertilizers.
Downloads: 13
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2008.03(1).07
Graphical Abstract: The paper describes the analytical potentialities of the trinuclear chromium(III) complexes as potentiometric ionophores for the construction of electrodes sensitive to the presence of nitrate anion. The electroactive material containing 4,4’-bipyridil was synthesized in situ. The membrane was prepared using dioctylphthalate as a solvent mediator and poly (vinyl chloride) as a polymeric matrix. The electrodes presented a slope of 56 mV/decade, a low limit of detection (3,2.10-6 mol/l), an adequate lifetime (4 months), and suitable selectivity characteristics when compared with other nitrate electrodes. The good parameters of this electrode made possible its application to the determination of nitrate in different types of fertilizers.
Downloads: 13
Author(s):
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2007 Volume 2, no.1
Pages: 51-57
Lavinia Tofan, Doina Bilba, Carmen Paduraru and Ovidiu Toma
Field: Analytical chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2007 Volume 2, no.1
Pages: 51-57
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2007.02(1).15
Graphical Abstract: The obtained results concerning the Ga (III) ion retention on flexible open cell polyurethane foam of polyether type pretreated with tri-n-butyl phosphate are presented. The influence of solution acidity, phases contact time, Ga (III) concentration and solution temperature have been investigated. The parameters of Ga (III) batch sorption have been optimized. On the basis of Langmuir isotherms, the sorption constants and the thermodynamic parameters, ∆G, ∆Η and ∆S have been calculated.
Downloads: 15
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3






