Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 84-93
Maimoonah Khalid Qasim, Rabah Ali Khalil
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 84-93
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1342
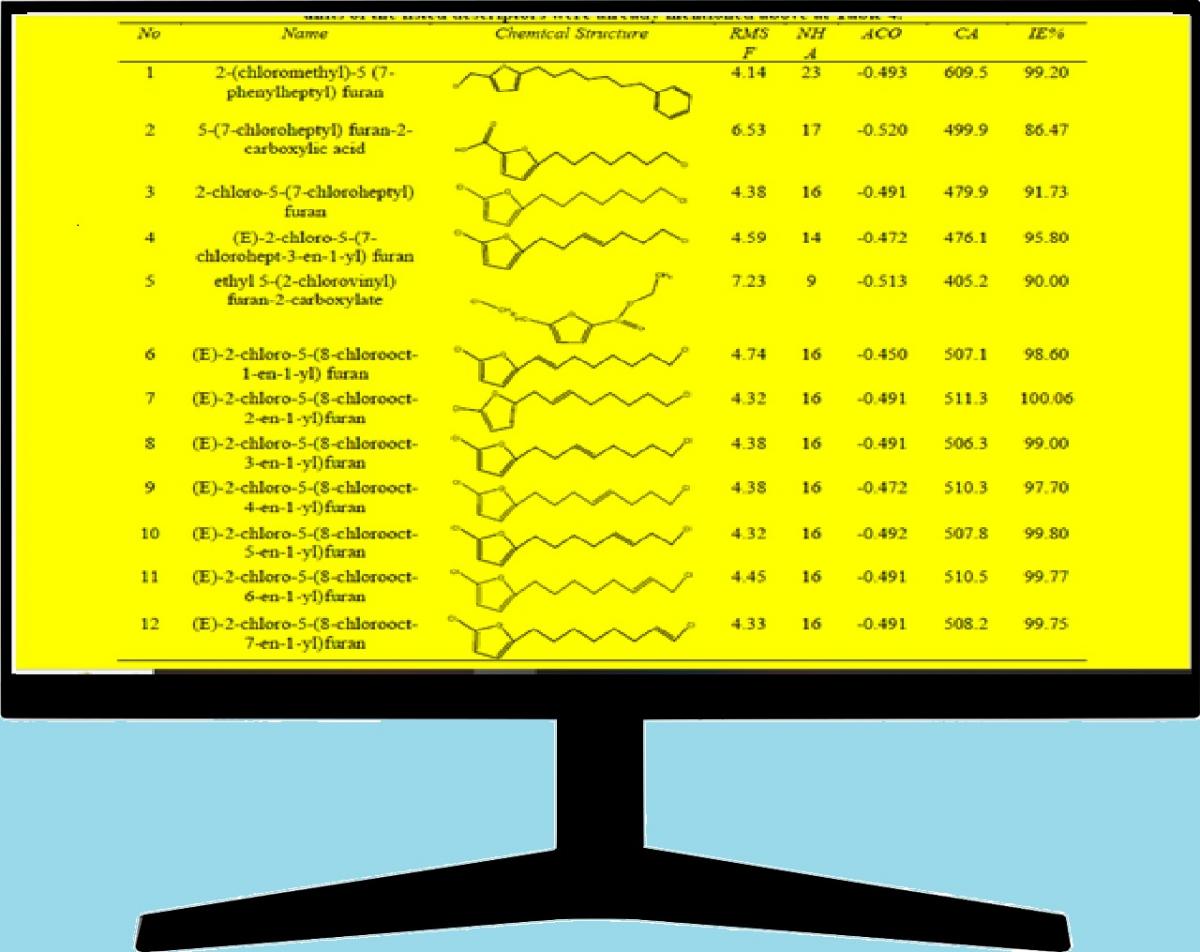
Graphycal Abstract: The contribution of in silico analysis in the development of corrosion inhibitors field by predicting adequate new molecules that could be employed for this purpose. QSAR analysis of already published experimental results of corrosion inhibition efficiency (IE%) of mild steel in acidic media for eighteen furan derivatives was performed.

Downloads: 24
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 69-78
Ihor Pylypenko, Iryna Kovalchuk, Mykola Tsyba, Yurii Lytvynenko, Oleksandr Shyrokov
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 69-78
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1294
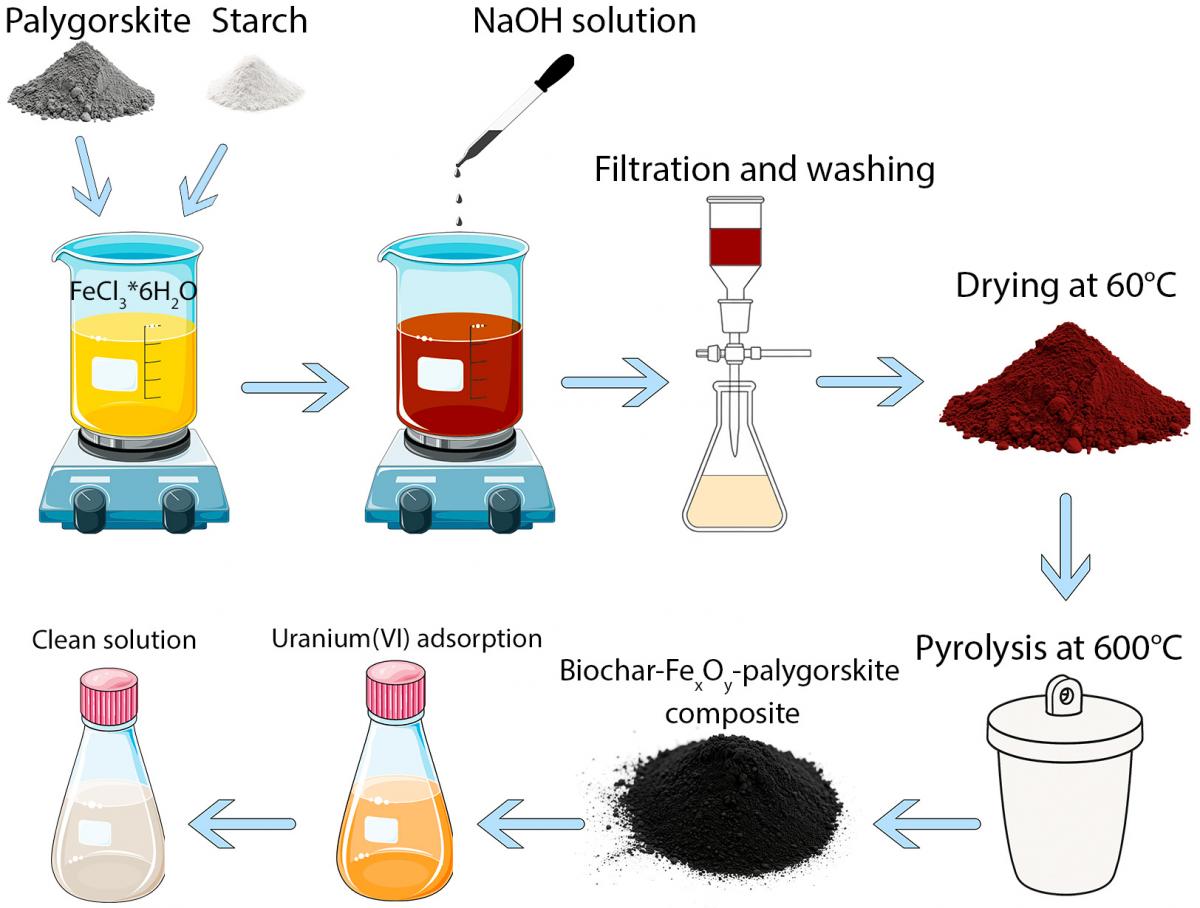
Graphycal Abstract: This paper presents palygorskite/biochar/iron oxide composites for uranium (VI) removal from water. The composites, containing magnetite and hematite, achieved maximum uranium adsorption (100.2 μmol/g), with pH increase enhancing the process. Magnetite facilitated uranium (VI) reduction to uranium (IV), proving effective for in situ water remediation.

Downloads: 79
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 79-85
Latifah Hauli, Chika Lutfi Adiningrum, Muhammad Safaat, Indri Badria Adilina, Silvester Tursiloadi, Lenny Marlinda, Dian Susanthy, Muflikhah Muflikhah
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 79-85
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1279
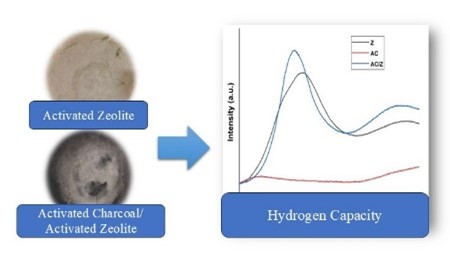
Graphycal Abstract: The purpose of this research was to activate Lampung natural zeolites, modify them with activated charcoal, and evaluate how well they store hydrogen. The highest hydrogen capacity value, 0.57 mmol/g, is found in activated natural zeolite, according to the Hydrogen-temperature programmed desorption data (H2-TPD).

Downloads: 45
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 86-94
Ibraheem Olusola Ayeni and Toyese Oyegoke
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 86-94
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1264
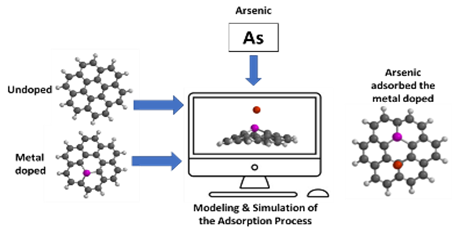
Graphycal Abstract: The impact of doping graphene with metals like Cu, Al, and Mn on its adsorption strength for arsenic (As) was computationally explored for industrial wastewater treatment. The results show that doped graphene outperforms undoped graphene, suggesting that doping can enhance the adsorptive properties of graphene for As removal.

Downloads: 76
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 93-100
Sergey Travin, Gheorghe Duca, Oleg Gromov
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 93-100
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1234
Abstract (PDF)
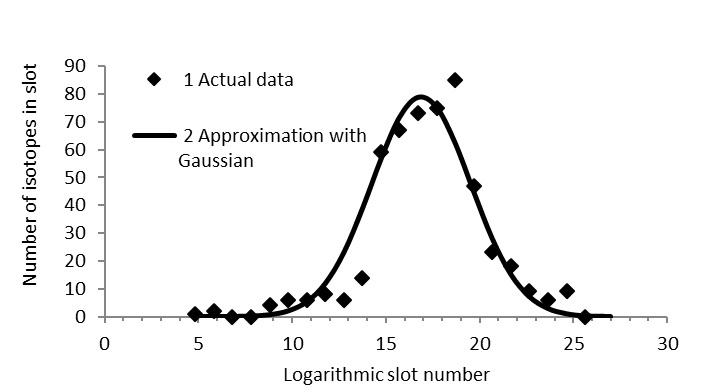
Graphycal Abstract: This study investigates the radionuclide emissions from nuclear power plants (NPPs), focusing on the gas-aerosol emissions from reactors such as VVER-440. The radionuclide composition of these emissions is analyzed to determine the biological hazards they pose, particularly focusing on isotopes such as tritium and radiocarbon. The research highlights the patterns of radionuclide accumulation in fuel assemblies using "rank-size" coordinates, which provide a more visual and informative method compared to traditional atomic weight dependency analyses.
Downloads: 70
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 93-101
Oleg Petuhov, Nina Timbaliuc, Irina Ceban (Ginsari), Silvia Cibotaru, Tudor Lupascu, Raisa Nastas
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 93-101
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.897
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
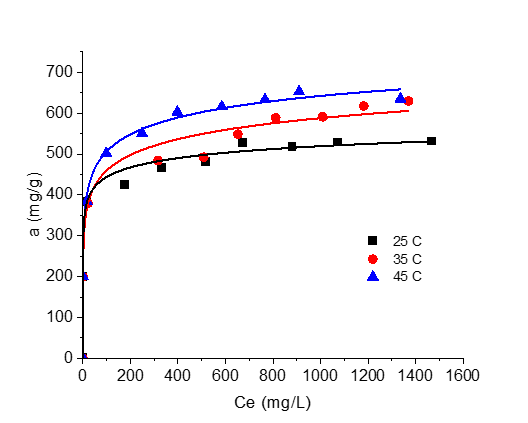
Graphycal Abstract: The purpose of this work was to compare the structural and sorption characteristics of local vegetal activated carbon obtained from apricot stones (AC-C, Republic of Moldova) with that of commercial activated carbons (Granucol® BI/GE/FA, Germany). According to the obtained results, the local vegetal activated carbon (AC-C) has proven to be comparatively effective with commercial ones (Granucol® type) in removing methylene blue dye from solutions.
Downloads: 277
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 84-92
Zainab Jasim Khudair and Zeina Mohammad Kadam
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 84-92
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1161
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
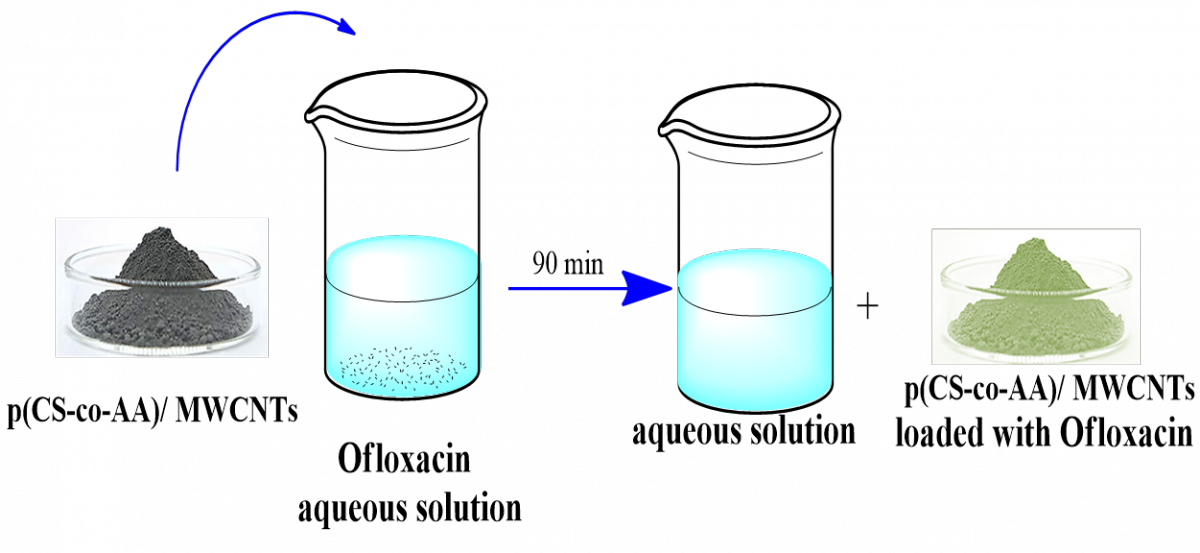
Graphical Abstract: A nanocomposite of chitosan and poly acrylic acid grafting multi-walled carbon nanotubesp (CS-co-AA)/MWCNTs was applied as adsorbent for Ofloxacin adsorption from water solutions. The isotherm constant (KF) of 0.218 and the separation factor (R2) of 0.956 indicate a strong and desirable adsorption of OFL on p(CS-co-AA)/MWCNTs with a concentration of 100 mg/L at a temperature of 293K and an acidic medium with pH of 7.0.
Downloads: 184
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 102-111
Sri Wuryanti, Tina Mulya Gantina, Annisa Syafitri Kurniasetiawati
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 102-111
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1157
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This research systematically investigates the impact of porphyrin and chlorophyll dyes derived from Syzygium Paniculatum on Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSC) performance, aiming to achieve maximum solar cell efficiency. The investigation involves utilizing fluorine-doped tin oxide coating with a TiO2-ZnO composite. Results demonstrate that DSSCs based on TiO2-ZnO: Al + chlorophyll produce an efficiency of 13.32%, while porphyrin (2:2:0.1) and (2:2:0.2) produce efficiencies of 8.91% and 13.95%, respectively. These findings highlight the potential of utilizing natural dyes for enhancing DSSC performance.
Downloads: 116
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 78-86
Ana Maria Toader, Maria Cristina Buta, Fanica Cimpoesu
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 78-86
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1146
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
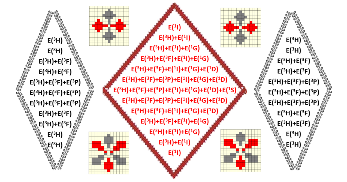
Graphical Abstract: The ab initio account of f and d electrons in lanthanide ions is assessed taking the Pr(III) ion. This shows rich experimental data and analytical tractability of spectral terms. The calculations are reaching a moderate match to experiment, the analysis identifying the actual impediments and suggesting ways of possible improvement.
Downloads: 119
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 96-104
Tudor Spataru
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 96-104
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1087
Abstract (PDF)
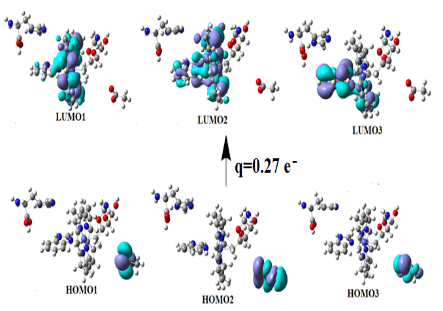
Graphical Abstract: The Pseudo-Jahn-Teller-Effect governs the glutamate mutase and methylmalonate-CoA mutase preliminary step and provides insight into particular details of in vivo C-N bond cleavage reactions of the adenosylcobalamin cofactor. Multi-configurational self-consistent field (MCSCF) calculations show that the preliminary step reaction glutamate mutase and methylmalonate-CoA mutase processes occur in the absence of total energy barriers.
Downloads: 67






