Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 87-95
Pedro Silva
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 87-95
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: DFT computations identify the effects that enable the synthesis of geometrically-strained epoxide from deprotonated halohydrins. These computations also explain the preference for the formation of larger cyclic ethers with five-atom rings over six-atom-rings. Increased temperature favors elimination over SN2 only when the reacting moieties are part of separate molecules.
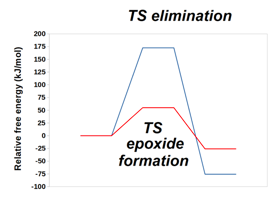
Graphical Abstract: DFT computations identify the effects that enable the synthesis of geometrically-strained epoxide from deprotonated halohydrins. These computations also explain the preference for the formation of larger cyclic ethers with five-atom rings over six-atom-rings. Increased temperature favors elimination over SN2 only when the reacting moieties are part of separate molecules.

Downloads: 116
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 69-77
Olga Chudinovych
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 69-77
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
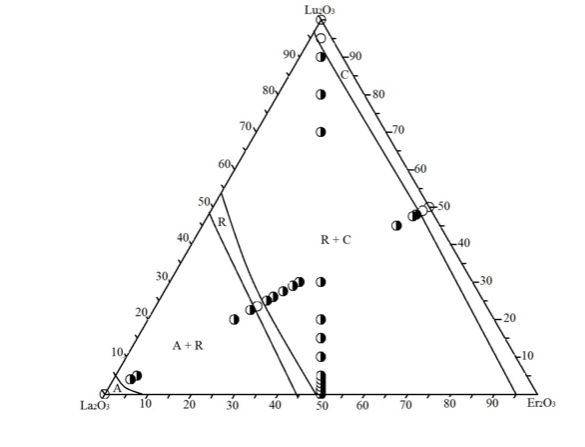
Graphical Abstract: The isothermal section of the La2O3–Lu2O3–Er2O3 phase diagram at 1250°C has the characteristic three one-phase fields (A-La2O3, R, C-Lu2O3(Er2O3)) corresponding to solid solutions based on starting components and two two-phase fields (C + R, A + R) between them.
Graphical Abstract: The isothermal section of the La2O3–Lu2O3–Er2O3 phase diagram at 1250°C has the characteristic three one-phase fields (A-La2O3, R, C-Lu2O3(Er2O3)) corresponding to solid solutions based on starting components and two two-phase fields (C + R, A + R) between them.
Downloads: 58
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Invited paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 7-14
Isaac Bersuker
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Invited paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 7-14
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This paper discusses the notion of symmetry of polyatomic systems defined as invariance under transformations, and showes that this important property of atomic matter is extremely vulnerable, and may undergo internal breakdown, subject to the presence of electronic degeneracy or pseudodegeneracy. It is shown that electronic degeneracy and its extended form, called pseudodegeneracy, are actually the only source of spontaneous symmetry breaking (SSB) in nature, including all forms of matter, beginning with elementary particles, via nuclei, atoms, molecules, and solids. Theoretically, the vulnerability of the notion of symmetry is due to the fact that, following quantum mechanics, the separation of the motion of electrons and nuclei (and, similarly, the separation of motions of elementary particles) is approximate, and hence the classical notion of polyatomic space configuration is approximate too, with SSB as one of its main violation.
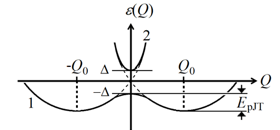
Graphical Abstract: This paper discusses the notion of symmetry of polyatomic systems defined as invariance under transformations, and showes that this important property of atomic matter is extremely vulnerable, and may undergo internal breakdown, subject to the presence of electronic degeneracy or pseudodegeneracy. It is shown that electronic degeneracy and its extended form, called pseudodegeneracy, are actually the only source of spontaneous symmetry breaking (SSB) in nature, including all forms of matter, beginning with elementary particles, via nuclei, atoms, molecules, and solids. Theoretically, the vulnerability of the notion of symmetry is due to the fact that, following quantum mechanics, the separation of the motion of electrons and nuclei (and, similarly, the separation of motions of elementary particles) is approximate, and hence the classical notion of polyatomic space configuration is approximate too, with SSB as one of its main violation.

Downloads: 73
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 120-124
Luciano Nascimento, Adriano Lima da Silva, Ana Cristina Figueiredo de Melo Costa
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 120-124
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: Amorphous alloy are materials have been around for some time and their applications can be found in many types of industrial products. Currently, the production of the amorphous alloy Co69Nb25B6 was obtained by high-energy ball milling which allows the formation of phases through solid state reaction through consolidation process. In addition, the effects of a 21:1 powder to ball mass ratio were used and the milling time during high energy milling was crucial for the formation of the amorphous and ferromagnetic phases. The characterization of the Co69Nb25B6 alloy was investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and by a vibrating sample magnetometer.
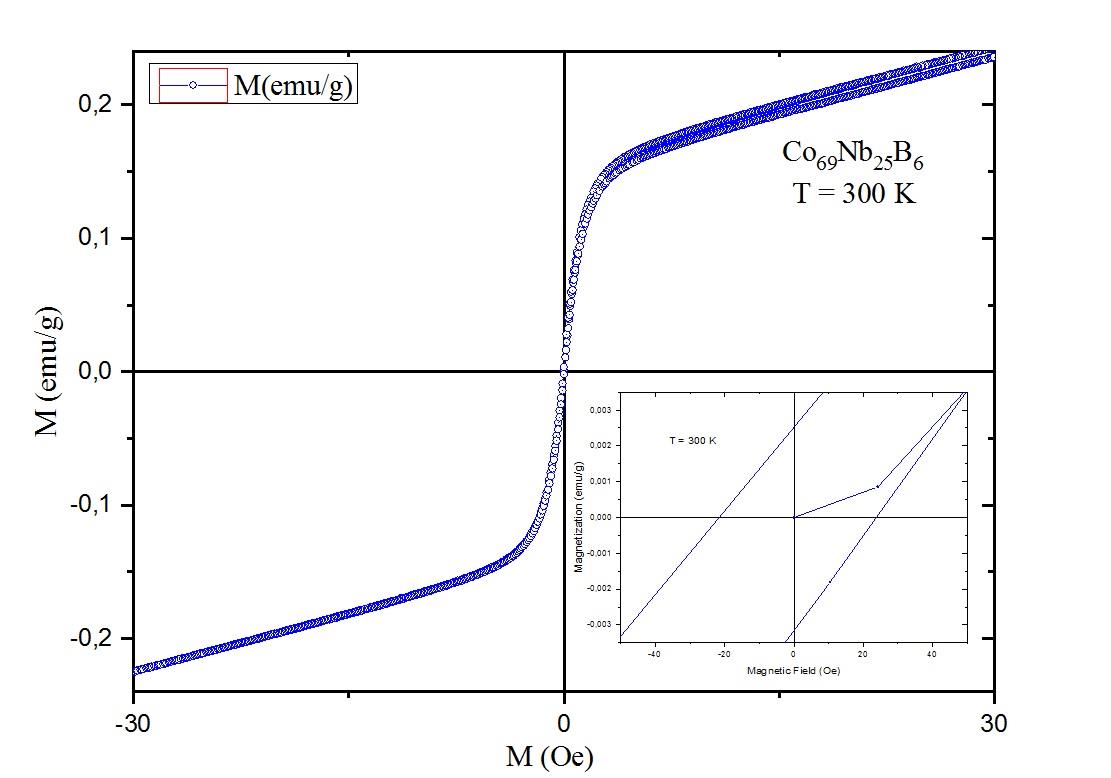
Graphical Abstract: Amorphous alloy are materials have been around for some time and their applications can be found in many types of industrial products. Currently, the production of the amorphous alloy Co69Nb25B6 was obtained by high-energy ball milling which allows the formation of phases through solid state reaction through consolidation process. In addition, the effects of a 21:1 powder to ball mass ratio were used and the milling time during high energy milling was crucial for the formation of the amorphous and ferromagnetic phases. The characterization of the Co69Nb25B6 alloy was investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and by a vibrating sample magnetometer.
Downloads: 140
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 47-55
Anna Nazar, Tatyana Rakitskaya, Tatyana Kiose
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 47-55
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The paper presents original results on the of nitric acid concentrations effect on structure, morphology, protolytic properties and the activity of low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysts based on acid-modified phlogopite (Н-Phl-1) and K2PdCl4, Cu(NO3)2, KBr base components. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, FT-IR spectroscopy and pH metric method. The obtained catalyst Pd(II)-Cu(II)/8H-Phl-1 can be recommended for use in respiratory devices.
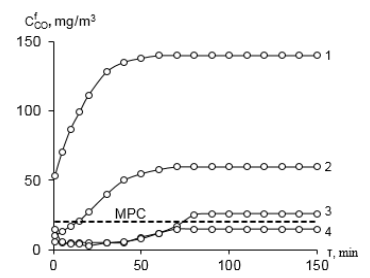
Graphical Abstract: The paper presents original results on the of nitric acid concentrations effect on structure, morphology, protolytic properties and the activity of low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysts based on acid-modified phlogopite (Н-Phl-1) and K2PdCl4, Cu(NO3)2, KBr base components. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, FT-IR spectroscopy and pH metric method. The obtained catalyst Pd(II)-Cu(II)/8H-Phl-1 can be recommended for use in respiratory devices.

Downloads: 185
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 37-46
Tatyana Rakitskaya, Alla Truba, Ganna Dzhyga
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 37-46
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The effect of halide ions (X= Cl−, Br−, I−) on the kinetics of ozone decomposition by compositions supported on the natural bentonite of the Dashukovske deposit in Ukraine (N-Bent(D)) has been studied. The obtained results have shown that the activity of the KX/N-Bent(D) composition in the ozone decomposition reaction increases in the row KCl << KBr < KI, which correlates with an increase in their reducing properties (the redox potential of the Х2/2Х− pair decreases). Such catalyst compositions can be recommended for applying in personal protective equipment for the respiratory system.
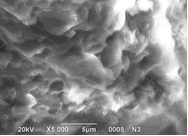
Graphical Abstract: The effect of halide ions (X= Cl−, Br−, I−) on the kinetics of ozone decomposition by compositions supported on the natural bentonite of the Dashukovske deposit in Ukraine (N-Bent(D)) has been studied. The obtained results have shown that the activity of the KX/N-Bent(D) composition in the ozone decomposition reaction increases in the row KCl << KBr < KI, which correlates with an increase in their reducing properties (the redox potential of the Х2/2Х− pair decreases). Such catalyst compositions can be recommended for applying in personal protective equipment for the respiratory system.

Downloads: 103
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 31-36
Alma Ryskaliyeva, Murat Baltabayev, Yerassyl Mukhamediyar, Rabiga Iskendirova
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 31-36
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: On the basis of a new model of chemical dissolution, an analysis of the kinetic parameters obtained using the modified V.V. Dolivo-Dobrovolsky equation was carried out. It shows that the change in parameters during the transition from one mineral to another is subject to a compensation effect. Additionally, calculations based on the new dissolution model made it possible to distinguish between the systemic and individual properties of minerals of the same nature in the process of dissolution. These minerals differ from each other by the concentration of ac tive surface complexes, and are combined into a system by a single transmission coefficient and the same value of the lifetime of the active complex.
Graphical Abstract: On the basis of a new model of chemical dissolution, an analysis of the kinetic parameters obtained using the modified V.V. Dolivo-Dobrovolsky equation was carried out. It shows that the change in parameters during the transition from one mineral to another is subject to a compensation effect. Additionally, calculations based on the new dissolution model made it possible to distinguish between the systemic and individual properties of minerals of the same nature in the process of dissolution. These minerals differ from each other by the concentration of ac tive surface complexes, and are combined into a system by a single transmission coefficient and the same value of the lifetime of the active complex.
Downloads: 106
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 24-30
Mikhail Gorbachev, Natalia Gorinchoy, Iolanta Balan
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.1
Pages: 24-30
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The detailed mechanism of the interaction of the radical cation ABTS•+ with a number of food acids (gallic, ferulic, caffeic, vanillic, cinnamic, syringic, p-coumaric) is revealed by means of the DFT calculations. It is shown that the interaction between the neutral molecules of the studied food acids and ABTS•+ does not lead to any charge transfer from these molecules onto ABTS•+. The almost complete conversion of the ABTS radical cation into its diamagnetic derivative occurs due to the interaction of one of the sulphonic groups of ABTS•+ with the acid anions through the formation of the corresponding intermolecular hydrogen bond.
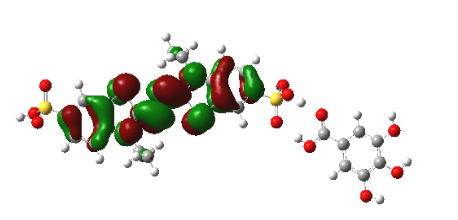
Graphical Abstract: The detailed mechanism of the interaction of the radical cation ABTS•+ with a number of food acids (gallic, ferulic, caffeic, vanillic, cinnamic, syringic, p-coumaric) is revealed by means of the DFT calculations. It is shown that the interaction between the neutral molecules of the studied food acids and ABTS•+ does not lead to any charge transfer from these molecules onto ABTS•+. The almost complete conversion of the ABTS radical cation into its diamagnetic derivative occurs due to the interaction of one of the sulphonic groups of ABTS•+ with the acid anions through the formation of the corresponding intermolecular hydrogen bond.

Downloads: 186
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2021 Volume 16, no.2
Pages: 102-111
Thamer Adnan Abdullah, Tatjana Juzsakova, Rashed Taleb Rasheed, Ali Dawood Salman, Mohammademad Adelikhah, Le Phuoc Cuong, Igor Cretescu
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2021 Volume 16, no.2
Pages: 102-111
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This paper deals with V2O5 nanoparticles adsorbents which were obtained by thermal pretreatment carried out by increasing the temperature between 90 and 750°C. In order to obtain more detailed information on the surface chemistry of the newly prepared nanoparticles, the characterisation was done by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric investigation technique. The prepared nanoparticles were tested for methylene blue (MB) removal from modelled water solutions. The obtained results indicated that increased MB removal efficiency (93%) and adsorption capacity (27 mg/g) after 40 minutes of adsorption were obtained for V2O5 annealed at 500°C. The applicability and suitability of the two kinetic models were tested and the removal mechanism was proposed.
Graphical Abstract: This paper deals with V2O5 nanoparticles adsorbents which were obtained by thermal pretreatment carried out by increasing the temperature between 90 and 750°C. In order to obtain more detailed information on the surface chemistry of the newly prepared nanoparticles, the characterisation was done by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric investigation technique. The prepared nanoparticles were tested for methylene blue (MB) removal from modelled water solutions. The obtained results indicated that increased MB removal efficiency (93%) and adsorption capacity (27 mg/g) after 40 minutes of adsorption were obtained for V2O5 annealed at 500°C. The applicability and suitability of the two kinetic models were tested and the removal mechanism was proposed.
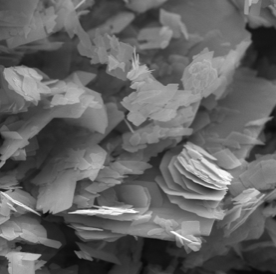
Downloads: 180
Author(s):
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2021 Volume 16, no.2
Pages: 91-101
Tatyana Rakitskaya, Tatyana Kiose, Lyudmila Raskola
Field: Physical chemistry and chemical physics
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2021 Volume 16, no.2
Pages: 91-101
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The effect of the nature and concentration of d-metal salts attached to synthetic zeolites NaA and KA on the kinetic and stoichiometric parameters of the chemisorption-catalytic oxidation of sulphur dioxide with air oxygen at ambient temperature was studied. It was found that the adsorption capacity of NaA zeolite relative to SO2 is 100 times higher than that of KA zeolite; the time of protective action of NaA and KA zeolites increases upon modification with transition metal salts and with an increase of their content in the compositions. It was shown that the formation of inner and outer sphere complexes and the relationship between them is determined by the nature and concentration of metal ions and by the nature of the carrier. It was proven that the chemisorption-catalytic process ends with the oxidation of SO2 to H2SO4.
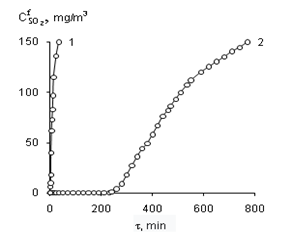
Graphical Abstract: The effect of the nature and concentration of d-metal salts attached to synthetic zeolites NaA and KA on the kinetic and stoichiometric parameters of the chemisorption-catalytic oxidation of sulphur dioxide with air oxygen at ambient temperature was studied. It was found that the adsorption capacity of NaA zeolite relative to SO2 is 100 times higher than that of KA zeolite; the time of protective action of NaA and KA zeolites increases upon modification with transition metal salts and with an increase of their content in the compositions. It was shown that the formation of inner and outer sphere complexes and the relationship between them is determined by the nature and concentration of metal ions and by the nature of the carrier. It was proven that the chemisorption-catalytic process ends with the oxidation of SO2 to H2SO4.
Downloads: 90






