Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Ecological chemistry
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2015 Volume 10, no.1
Pages: 20-24
Tatiana Mitina, Nadejda Bondarenco, Diana Grigoras, Elena Botizat, Tudor Lupascu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2015 Volume 10, no.1
Pages: 20-24
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2015.10(1).02
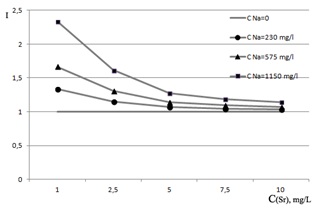
Graphical Abstract: This paper dwells upon the influence of sodium ions on experimental results regarding the concentration of strontium ions in waters with a high content of sodium ions by emission flame photometry and atomic absorption spectroscopy. The metrological characteristics of both methods are evaluated.
Downloads: 79
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2015 Volume 10, no.1
Pages: 25-32
Larisa Postolachi, Vasile Rusu, Tudor Lupascu, Alexei Maftuleac
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2015 Volume 10, no.1
Pages: 25-32
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2015.10(1).03
Graphical Abstract: The following factors which can improve the process of coagulation were studied: (i) the influence of stirring speed during coagulation and (ii) the influence of the concentration of the coagulant solution added in the process of coagulation. The coagulation process was studied on raw water of the Prut River. Application of the recommended procedure contribute to the reduction of the coagulant dose, the contact time, the aluminum concentration in water and the expenses for water treatment.
Downloads: 74
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 19-25
Oxana Spinu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 19-25
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).03
Graphical Abstract: On the basis of currently revised thermodynamic data for Cr(III) and Cr(VI) hydrolysis and photolytic equilibria in addition to original thermodynamic and graphical approach, used in this paper, the repartition of their soluble and insoluble chemical species has been investigated. By means of the diagrams “ΔG – pH”, the areas of thermodynamic stability of chromium(III) hydroxide have been established for a number of the analytical concentration of Cr(III) in heterogeneous mixtures. The obtained calculated results correlate well with existing experimental data.
Downloads: 50
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 26-31
Silvea Pruteanu, Petronela Spiridon, Viorica Vasilache, Ion Sandu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 26-31
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).04
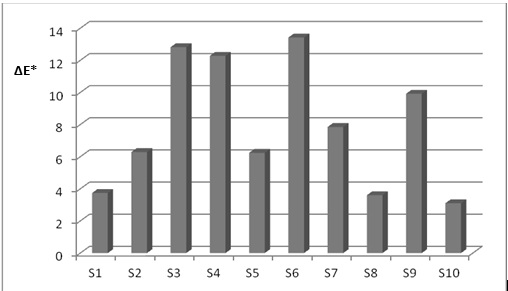
Graphical Abstract: Old icons, especially those involved in liturgical rituals are affected in time by external agents factors (temperature, humidity, light, pollution, microbiological attack, abrasion etc.), resulting changes of the appearance. Based on the literature in the field, a series of alcoholic solutions of different concentrations were made, as such or basified, which were compared with ecologic synergic systems based on organic uncolored vegetable juices and decoctions from dried plants. The cleaning effectiveness was done by visual analysis and CIE L * a * b * reflection colorimetry, this technique permitting to determine by color deviations the critical point where the patina and polychromy.
Downloads: 41
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 32-40
Alexandr Kоshev, Оlga Covaliova, Valery Varentsov
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 32-40
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).05
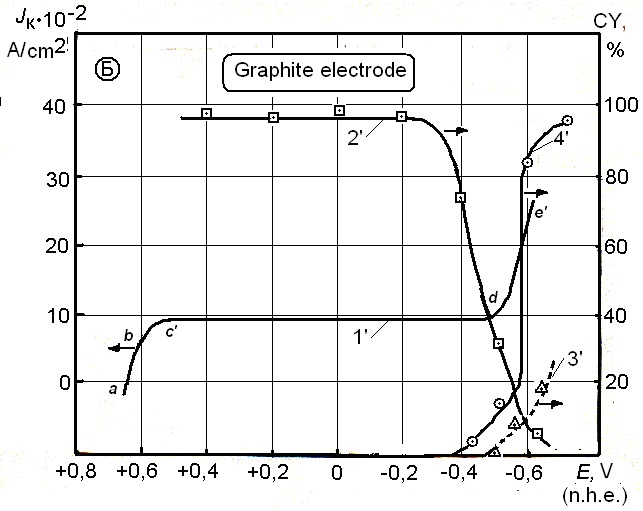
Graphical Abstract: The mathematical model of electrochemical processes distribution within the three-dimensional flow-through electrode for the system Fe(III)/Fe(II)/Fe is described in this paper, considering also the electrochemical reactions of hydrogen and molecular oxygen reduction. The results of calculations and experimental studies of iron electro-reduction are given, the analysis of the numerical modeling is provided.
Downloads: 37
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 41-51
Оlga Covaliova, Alexandr Kоshev, Valery Varentsov
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 41-51
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).06
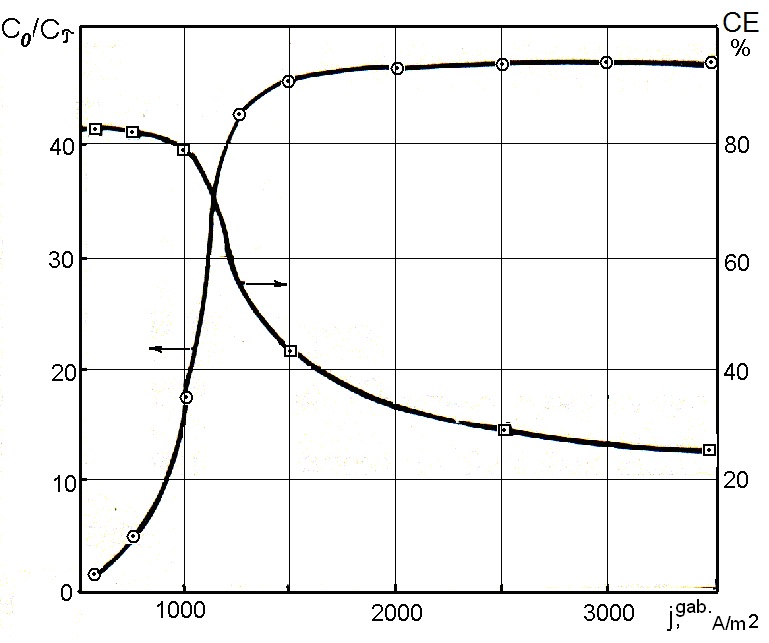
Graphical Abstract: The main regularities of the electroactive components distribution, polarization and local current density within the depth of the three-dimensional flow-through electrode have been studied using the calculation method, in dependence on the overall current density, electrode thickness and degree of its compression, solution flow velocity through the electrode, initial concentration of Fe(III) ions in the solution and electrodes brand.
Downloads: 31
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 52-57
Karen Ghazaryan, Hasmik Movsesyan, Naira Ghazaryan, Gor Gevorgyan, Karlen Grigoryan
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 52-57
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).07
Graphical Abstract: Kajaran town is situated in the south-east of the Republic of Armenia in Syunik Marz. Developed mining and smelting industries can be observed in this area. Six the most risky sites in this area and an unpolluted site as a control were selected for the study. The content of metals was determined by means of ELAN 9000 ICP-MS System. Study results revealed the increase up to 17 times in contents of following metals: Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cr, Sr, Mo, Cd, Pb, As. Experiments have led us to the assumption that pollution of soils with heavy metals in the studied territory is conditioned by human activities, particularly by mining and smelting industry.
Downloads: 47
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 58-61
Tudor Lupascu, Mihail Ciobanu, Victor Botan
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.2
Pages: 58-61
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(2).08
Graphical Abstract: Processes of removal of divalent ions of iron and manganese and hydrogen sulfide from groundwater at various pH values and temperature were studied. Obtained results have been used in order to elaborate a process of groundwater purification from the mentioned pollutants. The use of elaborated process for natural water leads to the decrease of the content of iron, manganese and hydrogen sulfide below the maximum allowable concentrations.
Downloads: 47
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.1
Pages: 33-36
Viktor Mukhin, Tudor Lupascu, Nadejda Voropaeva, Yuriy Spiridonov, Nicolay Bogdanovich, Vasiliy Gur’janov
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.1
Pages: 33-36
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(1).03
Graphical Abstract: Technologies for active carbons obtaining from vegetable byproducts such as straw, nut shells, fruit stones, sawdust, hydrolysis products of corn cobs and sunflower husks have been developed. The physico-chemical characteristics, structural parameters and sorption characteristics of obtained active carbons were determined. The ability of carbonaceous adsorbents for detoxification of soil against pesticides, purification of surface waters and for removal of organic pollutants from wastewaters has been evaluated. The obtained results reveal the effectiveness of their use in a number of environmental technologies.
Downloads: 77
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.1
Pages: 37-41
Nikolay Kornilov, Elena Kornilova, Elena Stepanenko
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2014 Volume 9, no.1
Pages: 37-41
Full Text (PDF): Download
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2014.09(1).04
Graphical Abstract: In the article the results of comparative analysis of the composition of the Eurasian hydromineral resources and the assessment of their impact on the physiological condition of a human organism according to biochemical studies of venous blood are presented. Processing of initial data on the composition and properties of mineral waters chloride-hydrocarbonate, sulphate- hydrocarbonate and chloride-sulphate types and venous blood are made using the method of mathematical modeling, developed by the authors of this article. It is shown that in the balneological impact of hydromineral resources on the body in the blood increases the hemoglobin and oxygen, decreases glucose, and acid-base pH shifted to high alkalinity.
Downloads: 46






