Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Ecological chemistry
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 7-14
Nina Bagrin, Elena Zubcov, Lucia Biletchi, Natalia Borodin
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.2
Pages: 7-14
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1341
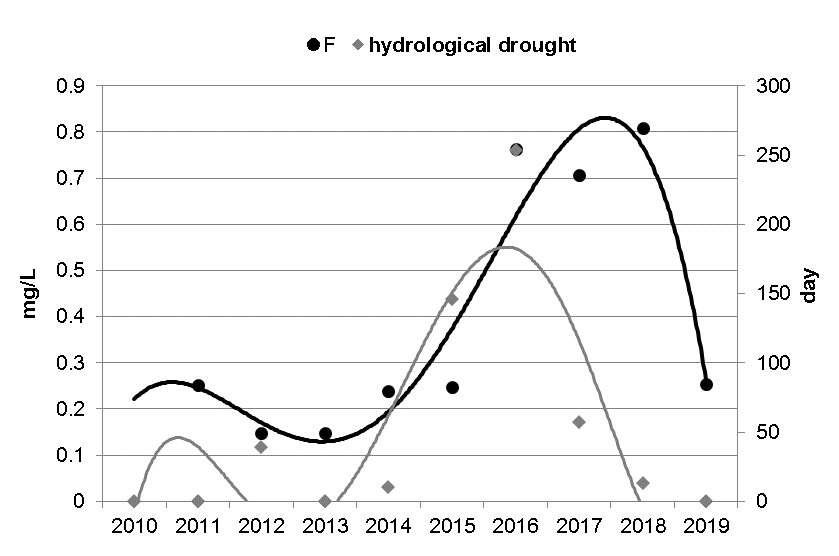
Graphycal Abstract: Concentrations of fluoride ions in the Dniester river and Dubasari reservoir, located on the territory of the Republic of Moldova, were analysed for 2011–2024. They ranged 0.05–1.07 mg/L, with higher values during low-water periods. Despite seasonal sampling, no clear dynamics were observed, due to altered hydrological regime. Fluoride levels were lower than the World Health Organization for drinking water.

Downloads: 31
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 17-27
Maxim Cisteacov, Gheorghe Duca, Vladislav Blonschi, Viorica Gladchi, Angela Lis, Elena Bunduchi
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 17-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
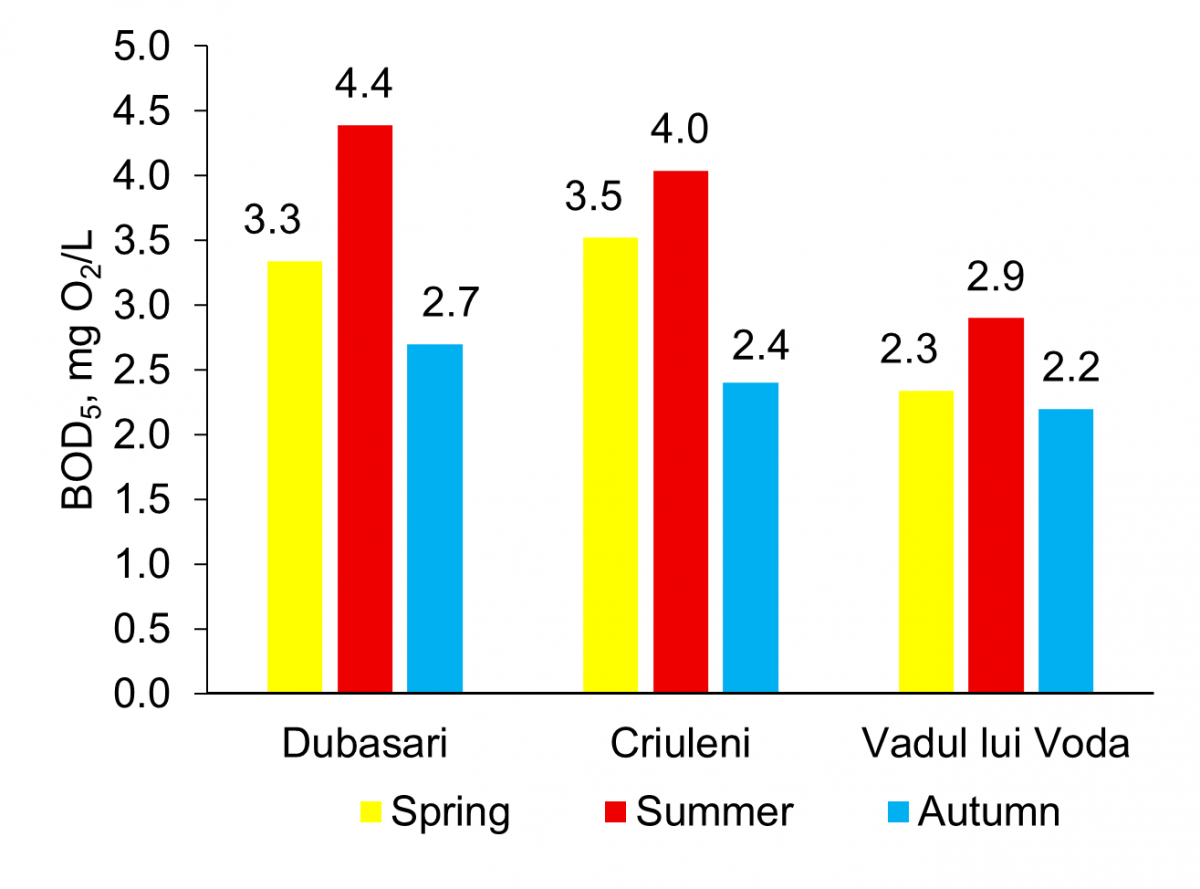
Graphycal Abstract: The study represents an analysis of the dynamics of self-purification processes in the Dniester River waters over ten years, conducted based on five hydrochemical and kinetic parameters. The study results demonstrated that the Dniester River waters are also loaded with reducing compounds, especially from the Răut and Ichel tributaries, which diminishes the intensity of the self-purification processes. However, after the last sampling point, a slight trend toward restoring initial properties was observed.
Downloads: 167
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Inna Trus, Vita Halysh, Mariia Tverdokhlib, Olena Makarenko, Evhen Chuprinov, Vadim Fedin
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Full Text (PDF): Download
Graphycal Abstract: A promising method of water conditioning for water circulation systems with the use of a scale stabiliser was considered. To inhibit the scale formation, antiscalant RT-2024-4 was used and the ability to mitigate the scale formation was tested. Water of various origins with different hardness was used during experiments.

Downloads: 56
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 95-99
Olha Khudoiarova, Oleg Blazhko, Alina Blazhko
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Short communication
Issue: 2025 Volume 20, no.1
Pages: 95-99
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2025.1250
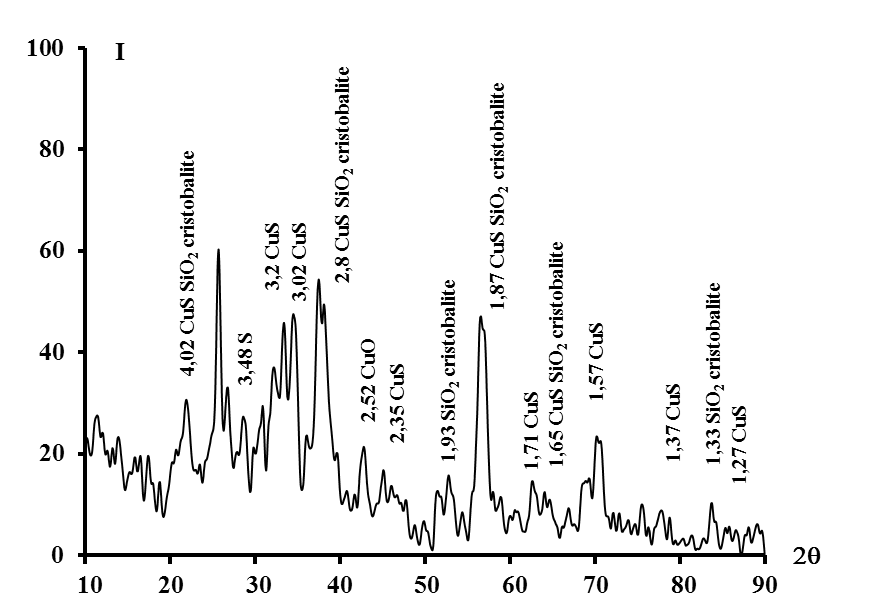
Graphycal Abstract: The effectiveness and prospects of using food industry waste sorbents for water purification from copper (II) ions have been studied. The use of a regenerated sorbent made of activated carbon and kieselguhr modified with sulphide and hydrosulphide ions increases the efficiency of removing copper (II) cations from water by 65.5 times It was established that topochemical reactions occur on the surface of the modified sorbent with the formation of copper (II) sulphide CuS and elemental sulfur. The possibility of topochemical transformations was established by IR-spectral and X-ray phase studies.

Downloads: 55
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 101-112
Victor Ciornea, Silvia Eftodi, Corneliu Cojocaru, Elena Zubcov
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 101-112
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1237
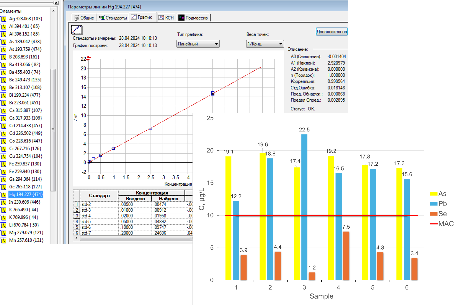
Graphycal Abstract: This study assessed water quality in Cișmea, Orhei district (coordinates 47°24’56.0"N 28°45’05.9"E). Surface and underground water were analyzed for pH, conductivity, hardness, chloride, sulfate, and chemical elements. The concentration values of the 36 elements determined by the ICP-OES method are presented. Conductivity and sulfate deviations indicated high dissolved solids. Results revealed significant deviations from permissible levels: As (1.7-1.9x), Cd (3.4-3.5x), Pb (1.2-2.3x), Na (1.2-4.0x), and B (1.6-3.3x). Notably, Ba, Tl, and Bi concentrations were also detected.
Downloads: 176
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 7-15
Nurfitrah Amran, Siti NurSyazwani Maadon, Yamin Yasin, Nik Rozlin Nik Masdek, Mohd Rafii Yusop, Nor Hazlina Mat Sa’at, Nor Monica Ahmad, Nor’Aishah Hasan
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.2
Pages: 7-15
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1196
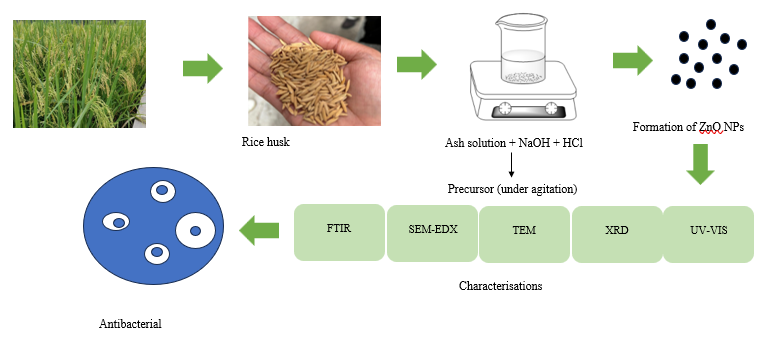
Graphycal Abstract: The present work explored the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using rice husk waste. The characterisation by UV-Vis spectroscopy suggested the formation of ZnO.
Analysis of X-Ray diffraction analysis (XRD) confirms the purity of the NPs with a crystallite size of less than 21 nm.Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy reveals the significance functional group at 487 cm-1.
Downloads: 60
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 56-61
Kaltrina Jusufi, Enju Wang, Taha Fadlou Allah, Ali A. Shohatee, Sudhir Kumar Singh, Makfire Sadiku
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 56-61
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1144
Abstract (PDF)
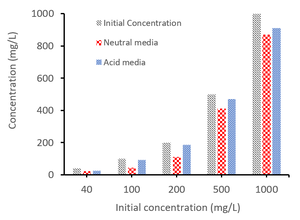
Graphical Abstract: This study examines the potential use of a low-cost biosorbent - chamomile tea residues, as an alternative to traditional adsorbents for removing Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions. The results show that lead concentration is reduced under optimized conditions, achieving an impressive nearly 50% Pb2+ ions removal with a mere just 0.05 g of the waste material, depicting chamomile tea residues as efficient biosorbent in lead removal.
Downloads: 108
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 47-55
Recep Taş, Ebru Köroğlu, Ahmet Karakuş, Ali Savaş Bülbül, Nilay Akkuş Taş
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2024 Volume 19, no.1
Pages: 47-55
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2024.1113
Abstract (PDF)
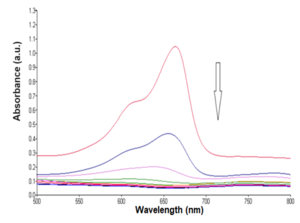
Graphical Abstract: This study explores the green synthesis of silver and zinc nanoparticles using Laurel extract as a reducing agent. The biosynthesized nanoparticles were characterized for size, shape, and structure. Photocatalytic activities were evaluated for potential environmental applications. Results show promising prospects for sustainable nanoparticle synthesis and efficient photocatalytic degradation.
Downloads: 873
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 15-27
Vladyslav Zhezherya, Petro Linnik, Rostyslav Linnik
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 15-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1091
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The aim of this research work was to evaluate the role of different fractions of humic substances in the binding of Al(III), Fe(III) and Cu(II) ions into complexes. The share of humic substances with a molecular weight of 20–5 kDa increases from 37% to 59%, when the total concentration of humic substances also increases. It was established that humic substances with molecular weight 20–5 kDa bounded the smallest amount of Al(III), Fe(III) and Cu(II) into complexes.
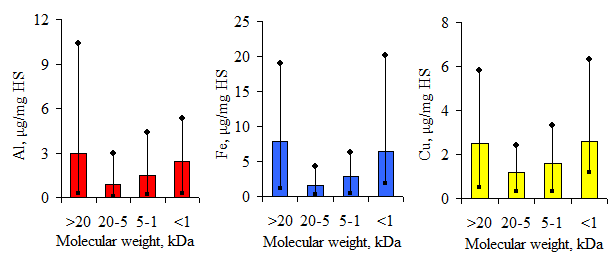
Downloads: 100
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 28-34
Muslim Hasan Allawi, Riyadh Sadeq ALMukhtar, Shurooq Talib Al-Humairi, Ali Dawood Salman, Tatjána Juzsakova, Viktor Sebestyén, Igor Cretescu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 28-34
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1019
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The degradation of diisopropyl methylphosphonate (DIMP) in aqueous solutions was studied using ultrasound irradiation with a fixed frequency of 26.6 kHz, following the first-order kinetic model. The experimental parameters, including the pH, the initial concentration of DIMP, the processing time, and the concentration of the additive CCl4 were investigated. The best degradation efficiency of 98% was observed at pH of 10, adding 0.8 g/L CCl4 for a processing time of 45 min.
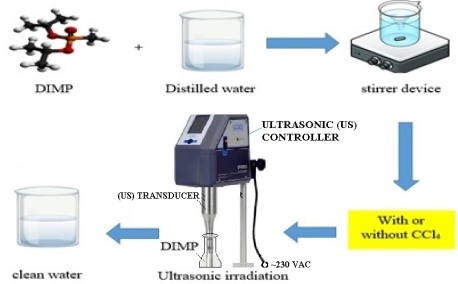
Downloads: 83






